Lung Cancer
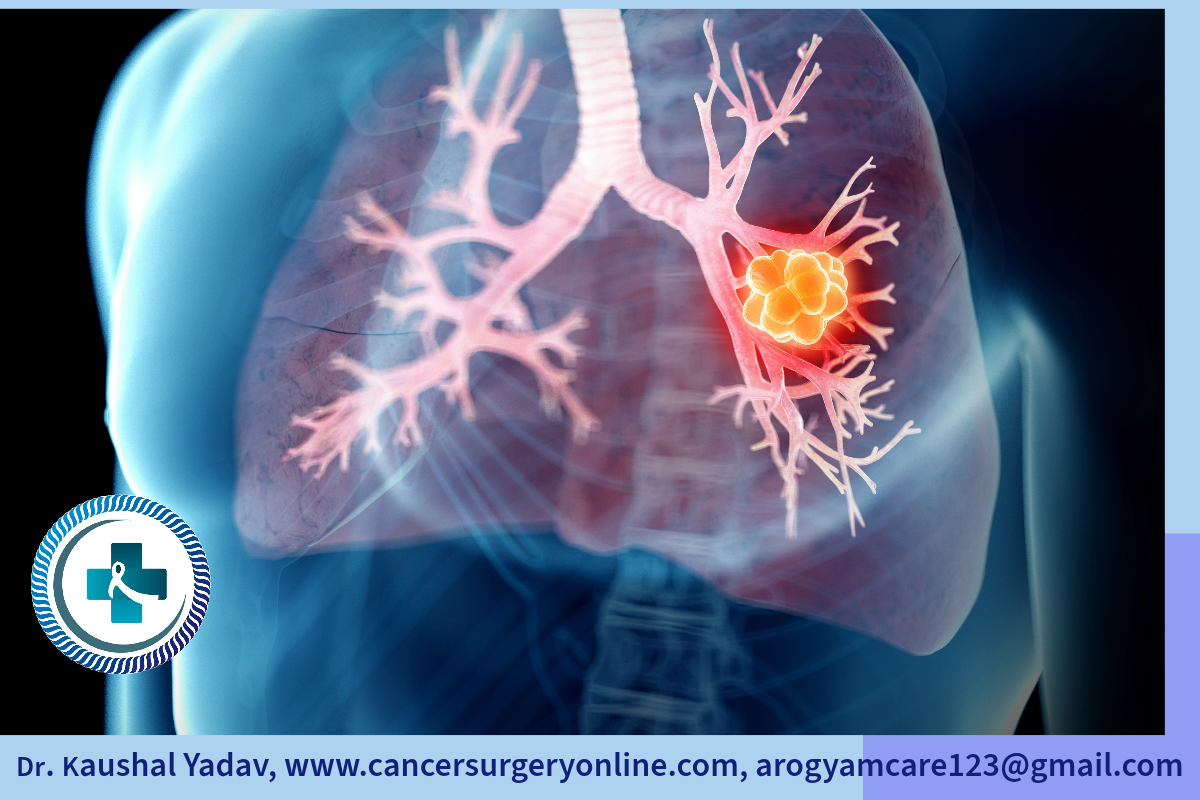
Lungs are the breathing organs of body and mutated cells proliferation in lungs leads to lung cancer.
- Lung cancer is most common cause of cancer related mortality worldwide
- In India, lung cancer constitutes 5.9 per cent of all new cancer cases and 8.1 per cent of all cancer related deaths in both sexes.
- As many as 2,500 persons die every day due to tobacco-related diseases in India
- Incidence of lung cancer is increasing more in metros with poor air quality
Types of lung cancer
Three are two main categories of lung cancer as explained by Oncologist. They grow and metastasize differently.
- Non Small Cell Lung Cancers – 85-90%. The most common subcategories are adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer- 10-15%. More aggressive and metastasize early.
Despite of poor prognosis, Lung Cancer is curable in early stages
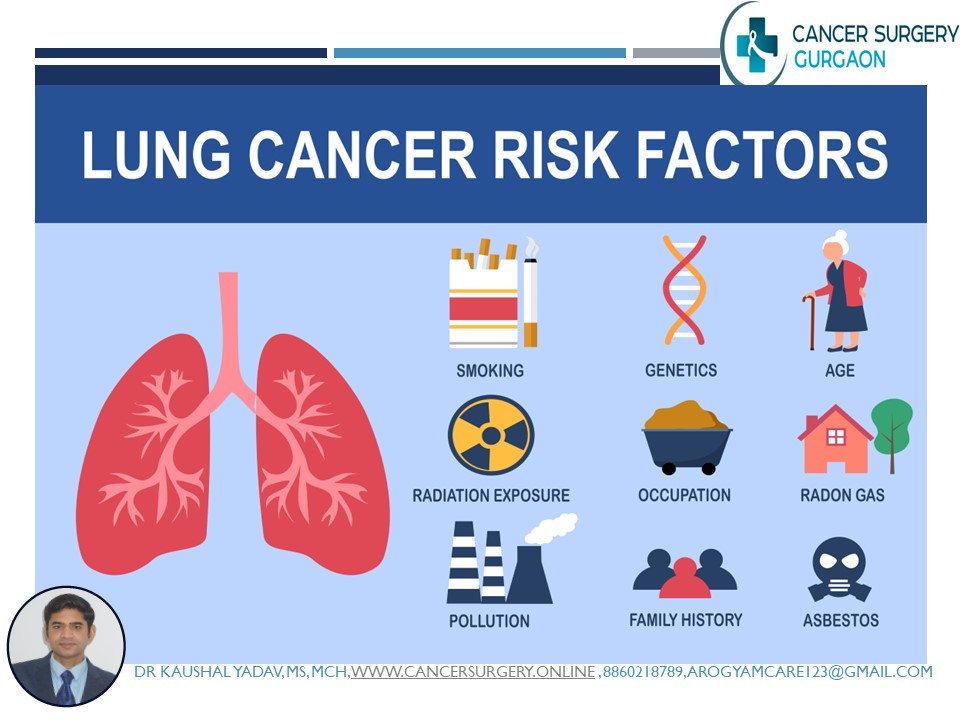
Risk Factors for developing lung cancer
- Smoking Tobacco – Smokers have 10-30 times more risk than nonsmokers. All forms of tobacco use are associated with lung, oral cavity and throat cancers. Risk increases with number and years. Stopping smoking reduce the risk of cancer.
- Asbestos and other chemical carcinogens
- Radiation exposure
- Environmental pollution
- Age – more risk after >40years
- Family History
- Chronic Lung disease
- Biomass fuel such as wood and coal burning
*Diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, fibers and that limits or avoids red and processed meats and sugary drinks probably lowers risk.
Screening for Lung Cancer:
Despite of poor prognosis, Lung Cancer is curable in early stages. So every attempt should be made to identify this disease in early stages.
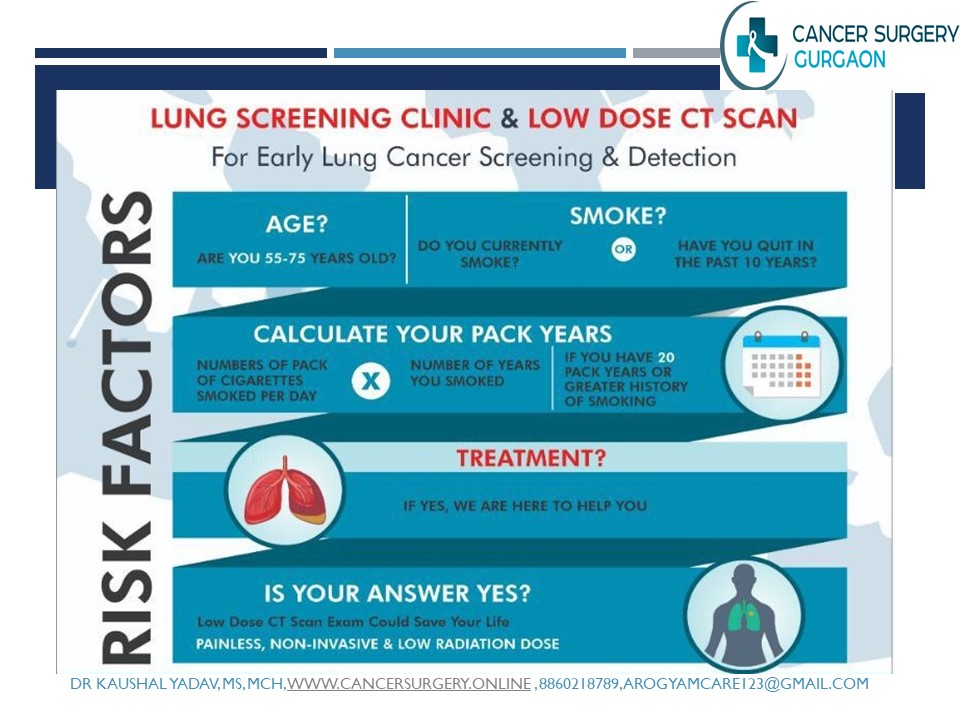
Screening is not recommended for everyone, but for some people with a heavy or long smoking history, screening can save lives.
Age group 55-80 yrs with a history of smoking
United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommend annual screening for lung cancer with low dose computed tomography in adults aged 55-80 years who have a 30 pack year smoking history and currently smoke or have quit within past 15 years. Screening should be discontinued once a person has not smoked for 15 years or develops a health problem that substantially limits life expectancy or the ability or willingness to have curative lung surgery.
Alarmimg Signs/ symptoms of Lung Cancer
Lung cancers are small in early stage and produce no symptoms. If advanced stages most people have one or more symptoms. If anyone have suspicion, they should immediately meet with their doctor for concern.
- Cough that is persistent or gets worse
- Chest pain that is often worse with deep breathing, coughing, or laughing
- Hoarseness of voice
- Coughing out blood or rust-colored sputum (spit or phlegm)
- Breathlessness
- Recurring infections such as bronchitis and pneumonia that don’t go away easily
- New onset of wheezing
- If lung cancer spreads to distant organs, it may cause Bone pain, headache/ seizures, jaundice
Investigations for lung cancer
Most coomonly done investigations to diagnosed lung cancer and as suggested by best of Surgical oncologists includes-
- Chest X ray
- CT Scan/ PET CT scan/ MRI: to assess primary disease extent and distant spread.
- Broncoscopy
- Biospy: to confirm the diagnosis and type of cancer. Either bronchoscopic or CT guided or from a superficaial lymph node.
Additional tests may also be done as per requirement of treating oncologist. Some of genetic and molecular markers used commonly include programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) translocations, and c-ROS oncogene 1 (ROS1) translocations. In this era of rapidly changing research, biomarkers and targeted treatment options will continue to change.
Staging of Lung cancer
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer: simplified staging-
- Stage 1: Cancer is limited lung.
- Stage 2: Cancer in the lung and nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage 3: Cancer from lung spread in mediastinal lymph nodes.
- stage 3A : lymph nodes on same side of the chest as primary cancer site.
- stage 3B : Cancer spread to lymph nodes on the opposite side of the chest or above the collarbone/ clavicle.
- Stage 4 : Cancer has spread to both lungs, into the area around the lungs, or to distant organs.
Small Cell Lung Cancer:- grow very fast.
- Limited stage – limited to one lung and nodes on same side of chest
- Extensive Stage – spread beyond or distant organs
Treatment of Lung cancer
Lung cancer is a complex cancer to treat even in early stages. Both disease status and patient’s performance status needs to assess properly and then treatment is advised. It is always beneficial to have physical activity/ breathing exercises and proper diet since to the start of evaluation.
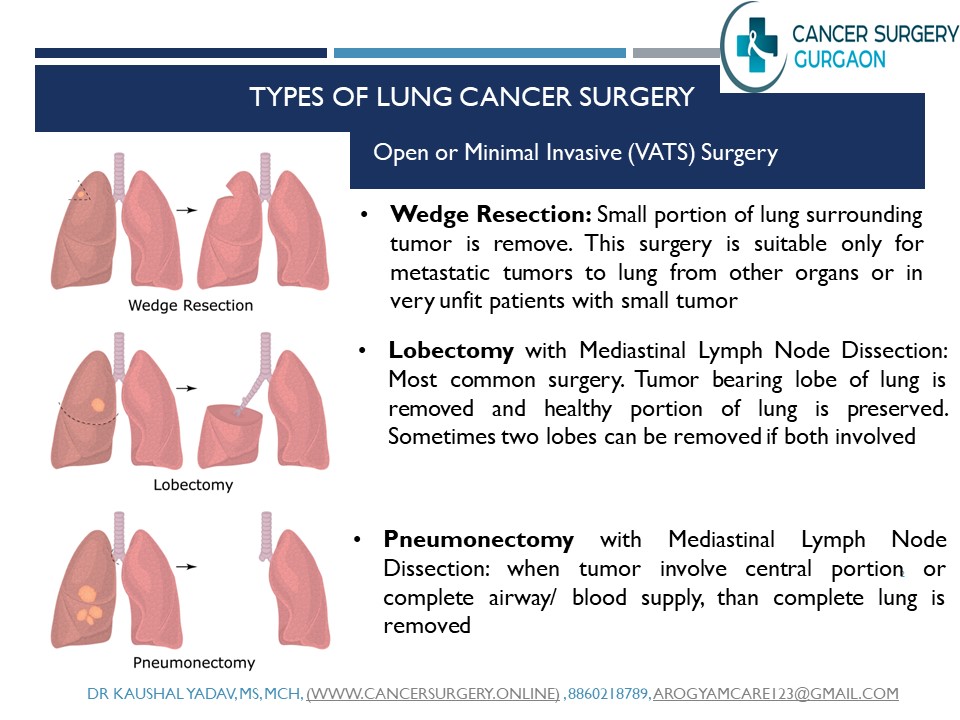
Surgery – Surgical resection is the curative treatment for lung cancer are usually done in stage 1 and stage 2.
- Lobectomy: Surgery usually invoves removal of lobe of lung along with removal of mediastinal lymph nodes.
- Pneumonectomy: Removal complete one lung if disease involve cental part and large disease along with mediastinal lymph node removal.
Whenever feasible surgery is preferred treatment, so a patient with lung cancer must be seen by a Surgical Oncologist to properly assess operability and curability. Sometimes surgical intervention is also required for palliation like thoracic cavity fluid drainage.
To Book Appointment for Cancer Surgery :
Integration of Multimodality Treatment
- Chemotherapy – helps in long term control of disease in early stages. In stage 4 chemotherapy or targeted therapy is the main treatment.
- Radiation Therapy – High energy Xray beams are used to kill cancer cells.
- Targeted treatment – designed to attack the cancer cells by attaching or blocking targets (specific proteins) that appear on the surface of the cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy – Immunotherapy has become the newest method of treatment for lung cancer in advance stages.
Small cell-lung cancer (NSCLC) treatment mainly includes radiation therapy. In most cases, the cancer will be too advanced for surgery.
Related Video
Got some questions
Although smoking is most common cause of lung cancer, but the persons who had never smoked can also develop lung cancer. Nonsmokers have 20 times less chances of developing lung cancer than smokers.
If detected in early stages lung cancer is completely curable with good long term survival
Low dose CT scan of chest is recommended screening test for lung cancer. Persons who are chronic smokers
Survival rates for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC) are:
Stage | NSCLC | SCLC |
Localized | 65% | 30% |
Regional | 37% | 18% |
Distant | 9% | 3% |
Please note that these survival rates are only estimates in general population and not a prediction of an individual person. Every person responds differently to treatment.