Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid is butterfly shaped organ located anteriorly in the neck in front of upper trachea. It produces thyroid hormone, it regulates body metabolism
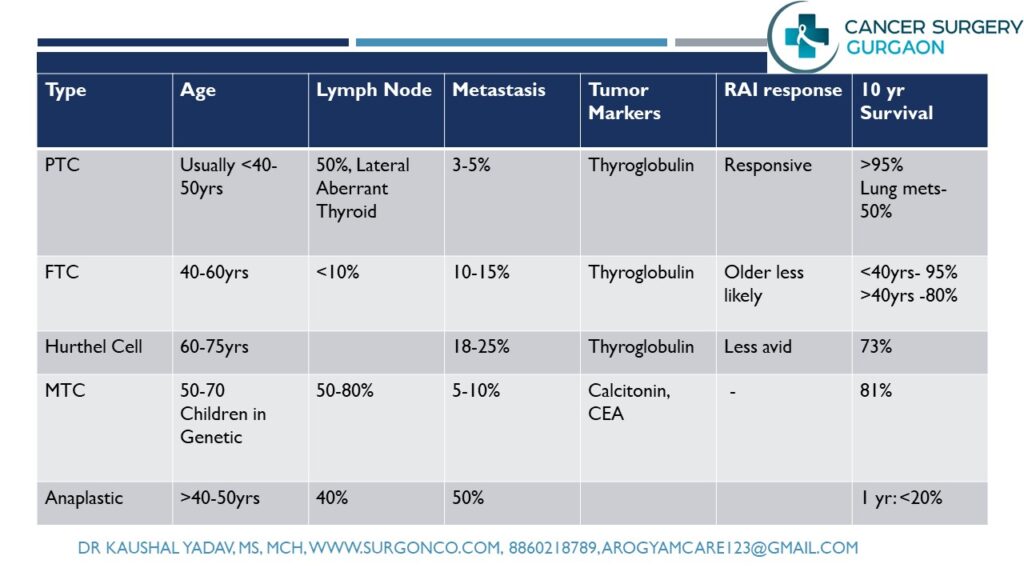
Types
Risk Factors
- Age
- Family History
- Inherited Conditions
- Radiation Exposure
- Obesity
Alarmimg Signs of Thyroid Cancer
- Thyroid cancer initially doesn’t cause any symptoms.
- Swelling in neck. Sometimes swelling is not in location of thyroid gland but on side of neck which is because of enlargement of neck lymph nodes by thyroid cancer cells
- Change of voice because of pressure over nerves
- Difficulty in breathing because of pressure over windpipe
- Difficulty in swallowing food because of pressure over foodpipe
- Pain in neck or throat
- Sometimes recurrent loose motions can be a presentation in medullary thyroid cancer
- In some cases thyroid tumors are also asoociated with other tumors like adrenal tumor in abdomen & parathyroid gland tumor in neck. Symptoms may be because of these tumors like high blood pressure, pain abdomen, excessive sweating, kidney stones.

Investigations
- Blood Tests includer Thyroid Function Test and Tumor markers like Thyroglobulin, Calcitonin, CEA.
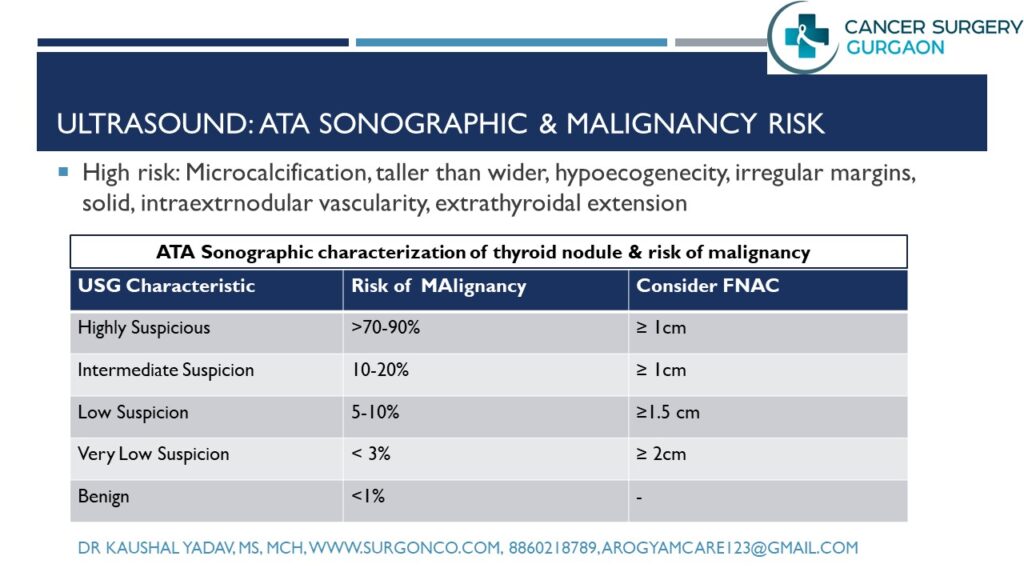
- Ultrasound Neck: is initial imaging and most useful investigation to know the nature of thyroid lesion.
- FNAC usually done under Ultrasound guidance and helpful in confirming diagnosis of cancer.
- CT Scan/ MRI/ PET CECT: to better characterize thyroid gland relations with nearby structure and for spread to other organs like chest and abdomen. It may also identify other associated tumors sometimes found in case of medullary thyroid carcinoma.
- Laryngeal Examination: As thyroid put pressure over voicebox nerves.
Some investigations may also be required to Check for associated tumors like in parathyroid gland or adrenal gland
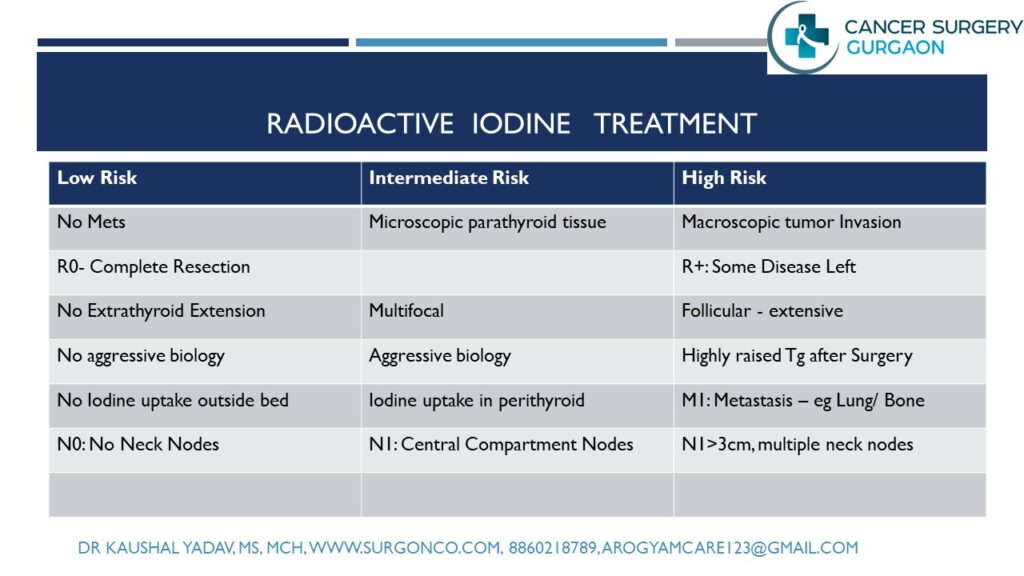
Treatment
Main Stay of Treatment for Thyroid Cancer is Surgery. Two types of surgery are advised – Thyroid Lobectomy & total Thyroidectomy.
- Thyroid Lobectomy: Removes disease bearing side of thyroid along with middle part of thyroid gland called isthmus. It preserves opposite healthy thyroid lobe. Lobectomy decrease the requirement of lifelong thyroid hormone replacement requirement. Thyroid lobectomy is usually done only for very small tumors which are around 1 cm or less and no other high risk features or neck lymph node spread
- Total Thyroidectomy: Removes the thyroid gland completely.
- The recurrent laryngeal nerve can often by dissected away from the tumor capsule, in most cases diseases can be removed away from these nerve but sometimes in case of nerve involvement with nonfunctional vocal cord recurrent laryngeal nerve may require nerve sacrifice. Voice box examination called laryngoscopy is import to assess function of vocal cords before surgery.
- Disease over windpipe (trachea) mostly can be removed away but when cancer goes inside trachea than resection of part trachea with rejoining is required
- Sometimes disease involve foodpipe which mostly can be treated with partial resection
- Parathyroid glans are located posteriorly over thyroid gland, there are four glands and these should be preserved always except in case of direct involvement by cancer. These glands are responsible for calcium metabolism in body. Temporary decrease in calcium level is common, rarely it can be permanent.
- Neck Lymph node Surgery: Lymph Nodes: Groups: Central (Near Trachea) & Lateral Lymph Nodes
- Patients with enlarged lymph nodes should undergo medial and lateral neck lymph node dissection. Patient with larger tumors should also undergo same side neck dissection and careful evaluation other lymph node regions their dissection if required
- In low risk group with no nodes on imaging and intraoperative assessment, neck dissection not required.
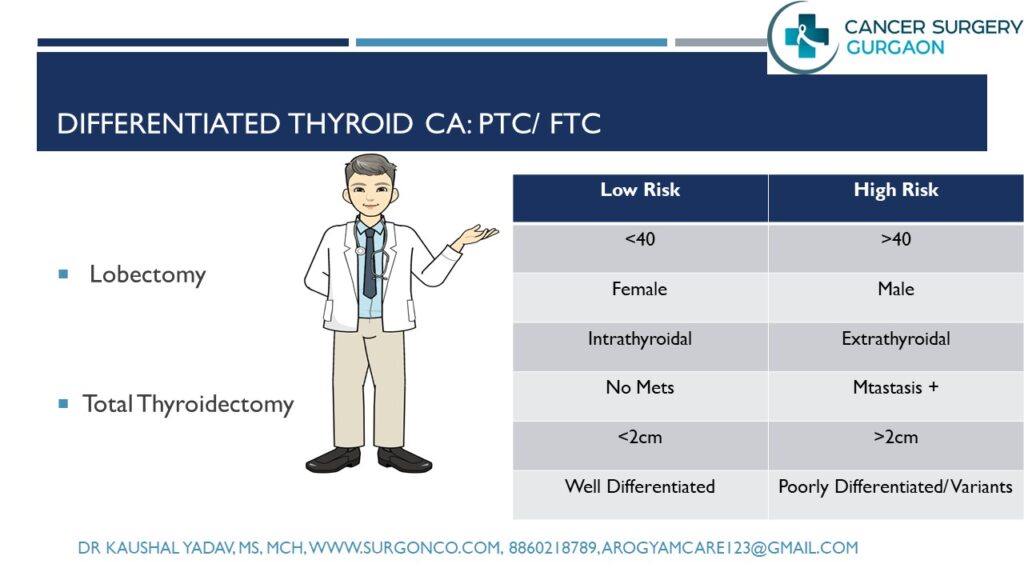
Risk Groups: High Risk: Females >45 yrs , Size > 1 cm, Incomoplete Resection, High Grade tumor, Extrathyroid Spread, Lymph Node and distant organ mets
Low Risk: Complete excision Size <1 cm, No nodes/mets, Low grade histology, High-grade follicular
- Diagnosis after proper evaluation confirm thyroid cancer on FNAC: Surgery
- Diagnosis of thyroid Cancer after Thyroid Lobectomy Surgery: If low risk can be observed, If in high risk group than completion surgery
- Diagnosis not confirmatory on FNAC: Frozen section analysis can be done at time of surgery. If positive than complete surgery. If negative no further treatment. If cancer on final report after surgery than appropriate surgery
-If low risk and small tumor than Close monitoring
-If high risk features than – Total completion Thyroidectomy
To Book Appointment for Cancer Surgery :
Integration of Multimodality Treatment
Got some questions
- If all relavant examination and investigations has been done than plan of treatment is finalized with colon cancer surgeon
- After deciding surgical procedure cost estimate can be taken from billing department or hospital. Clinic or hospital department coordinator will assist in case any help required. +918750587489,
- you can visit nearby hospital for colonoscopy screening as advised in our screening section or you can read various society guidelines like American cancer society, USPTF.
- You can consult us through our online consultation link. https://api.whatsapp.com/send/?phone=918750587489&text=I+am+Looking+for+an+appointment+with+Dr.+Kaushal+Yadav.+Please+Help&type=phone_number&app_absent=0