Blood Tests to detect cancer in early stages
Globally cancer cases are rising each year with more than 20% rise in last decade. Cancer is second most common cause of disease related mortality and soon it may become first. 1 in every 5 individual is at risk of cancer. Although 1 in every 6 death is caused by cancer but 90% of cancer are curable if detected in early and treated timely. Considering these scary figures many individuals ask if there is any blood test to detect cancer early? Do blood tests in health packages include have correct methods of cancer screening? There are various cancer tests available from blood samples. Let’s first understand what these different blood tests are.
.
1. Test for blood cells number
A complete blood count (CBC) measures the amount of each type of blood cell in a sample of blood. Blood cancers may be found using this test and Peripheral blood smear
2. Test for Chemicals or antigens Produced by Cancer: Tumor Marker Test
Tumor markers are substances, often proteins, produced by cancer cells or by normal cells in response to cancer in the body. They can be found in the blood, urine, stool, tumor tissue, or other tissues or bodily fluids. Tumor markers are most common cancer detection tests from blood samples. Tumor markers are used for various purposes such as:
- Screening and early detection of cancer
- Diagnosing certain types of cancer
- Predicting prognosis and how aggressive a cancer is likely to be
- Monitoring treatment effectiveness
- Detecting recurrence of cancer
Each tumor marker for cancer screening has its specific utility and is not necessarily conclusive on its own. Their utility as standalone blood test for cancer detection is not reliable. They are often used in conjunction with other tests to diagnose or monitor cancer. A tumor marker list commonly advised by cancer specilists includes:
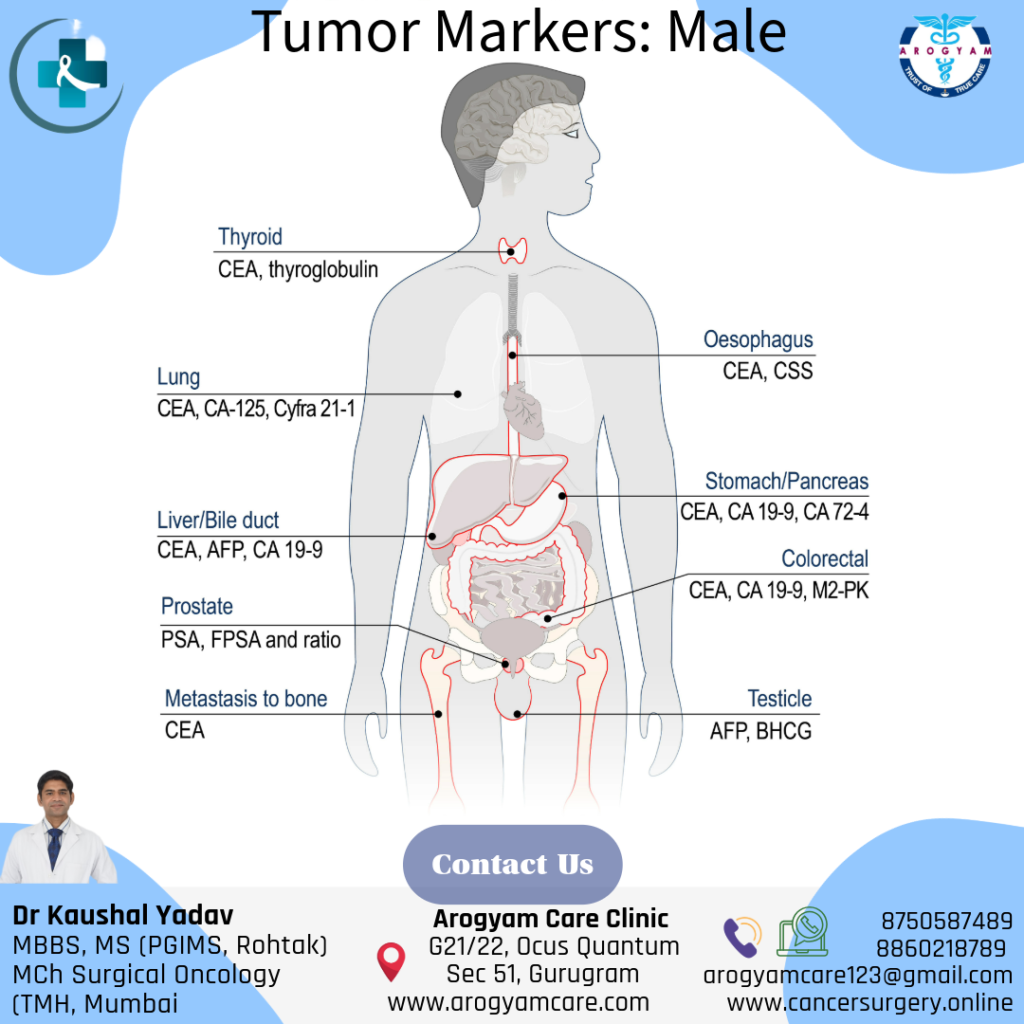
CA 125:
- CA 125 is primarily used as tumor marker blood test for ovarian cancer.
- Can also indicate other types of cancer such as endometrial, peritoneal, and fallopian tube cancer as blood tumor marker test.
- Levels can also be elevated in non-cancerous conditions like abdominal tuberculosis, endometriosis
- CA 125 normal range is upto 35 U/ml.
Human Epididymis Protein 4 (HE4):
- HE 4 along with CA 125 is Primarily used as tumor markers ovarian cancer.
- More specific than CA 125 but often used together for better accuracy.
- HE4 and CA 125 can be tested together as blood test of Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm (ROMA). Risk of cancer is high if ROMA value of > 13.3% in premenopausal females and > 76% in postmenopausal females presenting with adnexal masses.
PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen):
- Used to screen for and monitor prostate cancer.
- Elevated levels can also indicate benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostatitis.
- Upper limit of normal range of PSA is generally considered as upto 4ng/ml, but in males below 60 years of age it can be considered as 2.5-3ng/ml.
- Free PSA level is also utilized at many centers. If free PSA is >25% than risk of prostate cancer is more.
- PSA along with DRE is recommended screening methos for males from 50-75 years by various bodies.
CEA (Carcinoembryonic Antigen):
- CEA is tumor markers for colorectal cancer primarily, but also for breast, lung, and pancreatic cancers.
- Indicates whether cancer is growing/spreading or diminishing with treatment.
- Elevated levels can also be seen in non-cancerous conditions like inflammation.
- CEA normal range is upto 2.5ng/ml for nonsmokers and 5ng/ml for smokers
CA 19-9:
- CA 19-9 is mainly used as tumor marker for pancreatic cancer, gall bladder cancer and bile duct cancer.
- Bile duct cancers are knowns as Cholangiocarcinoma. Cholangiocarcinoma can be outside the liver in bile ducts and it can also occur inside the liver as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma,
- Elevated levels can be seen in pancreatitis and liver diseases.
- CA 19-9 normal range is upto 37 U/ml
CA 15-3/CA 27.29:
- Tumor marker for breast cancer monitoring.
- Helps evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
- Levels can rise in benign breast conditions.
AFP (Alpha-fetoprotein):
- Serum AFP is the primary tumor marker of the most common type of liver cancer- hepatocellular carcinoma.
- AFP is also primary tumor marker of germ cell tumors. Germ cell tumors arise from testis in males and ovaries in females. They are more common in young age group.
- Levels are checked before and after treatment to see its effectiveness.
- Serum AFP levels can also rise in Liver related infections and diseases..
- Normal value of S. AFP is 0-10ng/ml
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH):
- LDH is also a tumor marker of germ cell tumors. These germ cell tumors arise from testis in males and ovaries in females.
- Elevated in various cancers including lymphoma, leukemia, melanoma, and neuroblastoma.
- Also rises in non-cancerous conditions like hemolysis or liver disease.
- Normal range of LDH is 140-280 U/ml.
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG):
- Beta hCH is used to diagnose and monitor germ cell tumors, like testicular cancer, ovarian germ cell tumors.
- Elevated in trophoblastic disease and some ovarian cancers.
- Also measured during pregnancy.
Thyroglobulin:
- S. thyroglubulin is tumor marker of well differentiated thyroid cancers like papillary thyroid cancer and follicular thyroid cancer.
- Used to check for recurrence after treatment.
- Can be elevated in thyroiditis and hyperthyroidism.
Calcitonin:
- Specific marker for medullary thyroid cancer (MTC).
- Levels increase with thyroid neoplasms.
- Can be part of genetic predisposition (like MEN2) or spontaneous mutation.
Beta-2-Microglobulin (B2M):
- blood test for multiple myeloma and lymphoma.
- Can indicate kidney disease when elevated.
- Used to assess prognosis and treatment response.
These markers are part of a comprehensive diagnostic and monitoring strategy for cancer patients. They help in assessing the presence of cancer, the effectiveness of treatments, and can sometimes provide prognostic information. But these should not be interpreted as stand alone test. They are helpful when combined with examination and imaging. U
3. Test for proteins in blood: Serum Electrophorosis
An electrophoresis blood test looks at the various proteins in your blood to find the ones made by your body’s germ-fighting immune system. This test helps diagnose multiple myeloma.
4. Test for blood genetic material in blood: liquid Biopsy
As the tumor grows its parts break and circulate in blood stream. Liquid biopsy is a blood test that detects these materials from cancer. This cancer genetic material can be Circulating tumor cell (CTC) or Circulating tumor DNA (CtDNA). They are mostly used in advanced stage of cancer rather than for early detection of cancer.
5. Multicancer Early Detection Tests (MCED):
- Screening tests are available and advised for few cancers that are responsible for only approximately 25%–30% of all cancer-related deaths. MCED tests can provide a screening modality for lethal cancers that have no effective tests. These cancers are responsible for 70%–75% of all cancer deaths and finding these cancers at an early stage is the major purpose of these tests.
-
 An additional value of MCED testing is to find common cancers that are either missed by standard screenings or detect these cancers in people who are not utilizing standard screening. One of these tests available in India is PANTUM detect blood test for cancer which identifies Apo10 and TKTL1 proteins in white blood cells. MCED test does not identify the location and type of cancer. If MCED test is positive than appropriate imaging like CT scam/ MRI or PET scan and biopsy is required for proper diagnosis of cancer
An additional value of MCED testing is to find common cancers that are either missed by standard screenings or detect these cancers in people who are not utilizing standard screening. One of these tests available in India is PANTUM detect blood test for cancer which identifies Apo10 and TKTL1 proteins in white blood cells. MCED test does not identify the location and type of cancer. If MCED test is positive than appropriate imaging like CT scam/ MRI or PET scan and biopsy is required for proper diagnosis of cancer
Recommendation for Eatrly detection of Cancer
Individuals should continue to follow recommended cancer screening guidelines and consult their doctor for an annual MCED test. Various blood tumor markers and other tests should be done only after consultation with the doctor. These tests should for interpreted only in consultation with an Oncologist nearby because these tests may also be raised in certain noncancerous conditions also.
To Know more about Early Cancer Diagnosis
Discover more from CancerSurgery
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.