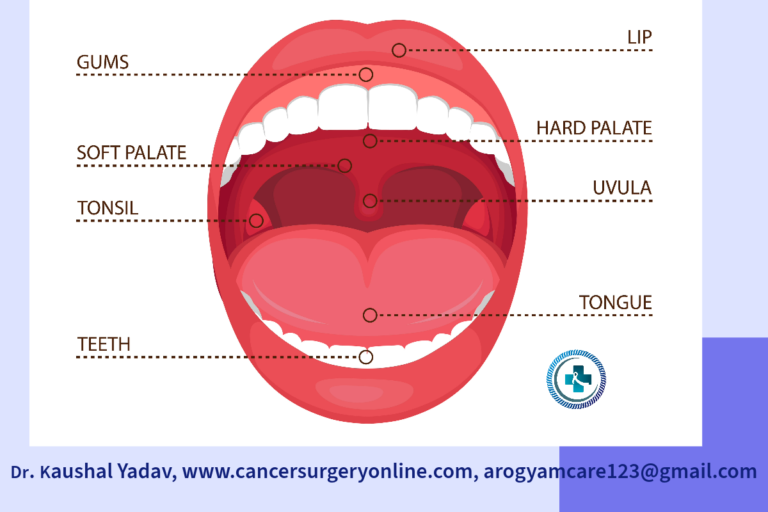
Oral Cancer
Incidence of oral cancer: How common is oral cancer?
- India has almost 1/3rd of cases of oral cavity in world.
- Oral cancer accounts for approx. 10.3% of all cancers in India
- Oral cancer is most common cancer in Indian males and 4th most common in Indian females. Overall oral cancer is 2nd most common cancer in India.
- Oral cancer is 2nd most common cause of cancer related deaths in India.
Risk Factors: Oral Cancer
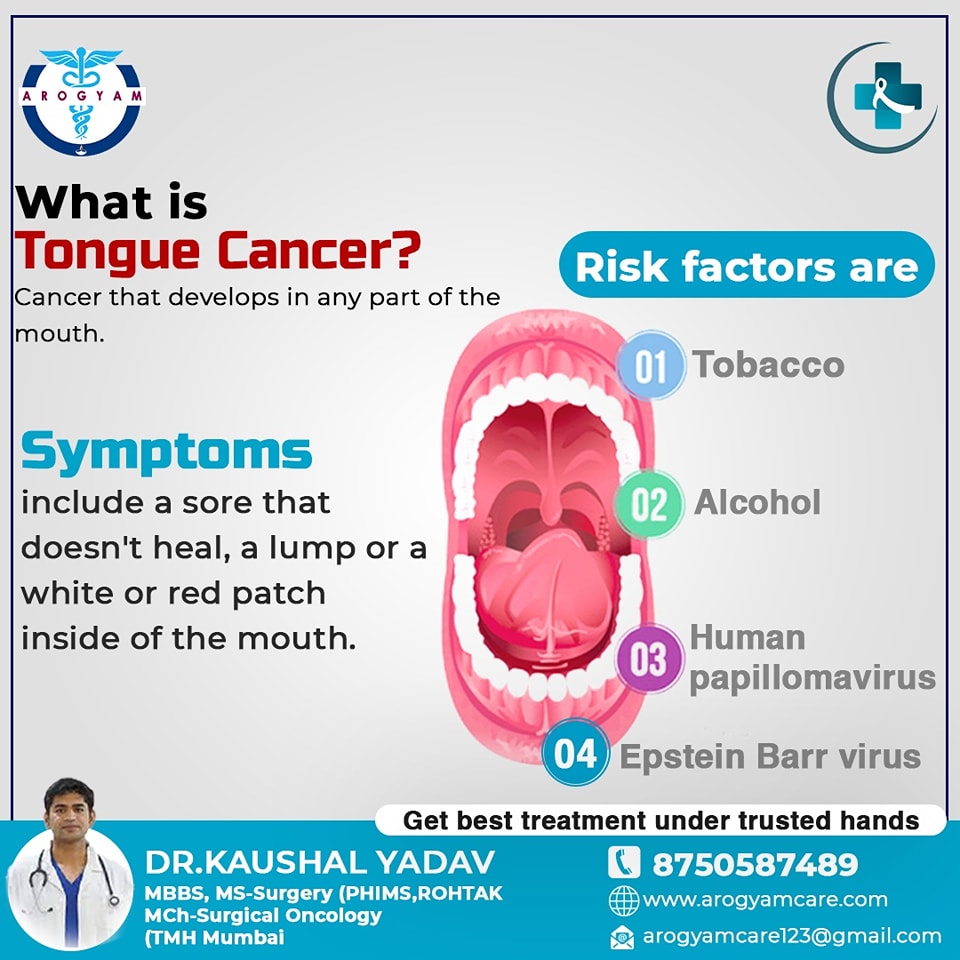
- Tobacco in any form smoking or smokeless in the form of jarda, ghutka etc.
- Betel nut with or without paan
- Alcohol
- sharp teeth or dentures causing constant irritation
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) Infection
- Poor oral hygiene
- Leukoplakia – a condition characterized by a whitish patch that develops inside the mouth or throat.
- Erythroplakia – a condition characterized by a red, raised patch that develops inside the mouth.
- Excessive sun exposure, which, like elsewhere on the body, can cause cancer on the lip
Early Signs of Oral Cancer: Oral cancer symptoms
An ulcer or sore that does not heal or bleed on touch
a white or red patch on the gums, tongue, or lining of mouth
a lump on the lip or in the mouth or throat
unusual bleeding, pain, or numbness in the mouth area
Restriction in opening mouth- submucosal fibrosis
Unusual bleeding from nose
Swelling of the jaw
pain in the ear
change in voice
a chronic sore throat
a feeling as if something is caught in the throat
pain or difficulty in swallowing or chewing
Loosening of tooth or ill-fitting of denture
Oral Cancer Screening:
Investigations of oral cancer
- Physical examination of oral cavity and entire body, including health habits and past illnesses and treatments
- Endoscopy is an examination of areas of the throat, pharynx and larynx with a thin, lighted tube
- Biopsy is the removal of tissue samples to look for signs of cancer
- Computerized Tomography (CT) scans of face/ neck and distant sites chest; abdomen produce images of the size and location of tumors and metastases, or places where tumors have spread.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): uses radio wave pulses to make images of spatial variations in the absorption and emission of energy between healthy tissue and tumors.
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan uses radioactive sugar molecules injected intravenously. Cancer cells absorb sugar more quickly than normal cells, so they “light up” on the scan.
Treatment of oral cancer
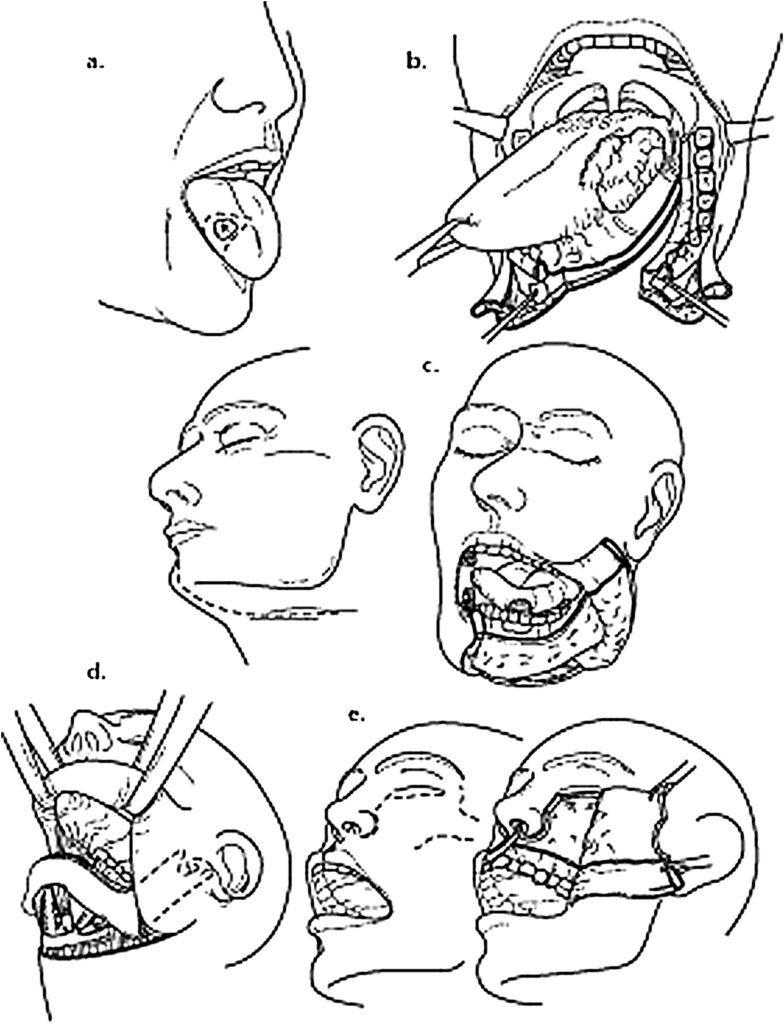
Surgery: When surgery is the main option for cure and treatment of oral cancer, the whole tumour and the lymph nodes are removed. Surgery is commonly used to remove cancer for all stages of cancer of the oral cavity. Reconstructive surgery restores function or improves the appearance of parts of the body. It may include dental implants, skin graft, local flap or free flap.
- Wide Excision: Depending on the afflicted area Wide Excision may include a surrounding structure also. For e.g., in some cases, a rim or segment of the jaw bone may be removed so that there is no compromise on getting a microscopic clean margin.
While the Oncosurgeon is totally focused on getting the tumour out, he/ she would have a plan for reconstruction which is often discussed with a plastic surgeon and the patient, in advance. Loss of tissue expected and the plan for reconstruction should discussed with Surgical Oncologist and reconstructive surgeon. - Neck Lymph Node Dissection – Head & Neck Cancers generally spread to neck glands. Even if the neck glands are not involved, these might have to be removed for control of cancer. Selective or modified neck lymph node dissection is done so that the appearance and shoulder function are well preserved.
To Book Appointment for Cancer Surgery :
Integration of Multimodality Treatment
Radiation therapy uses high-energy x-rays to kill cancer cells.
Chemotherapy uses drugs taken by mouth or injections through a vein or muscle to stop the growth of cancer cells. The way that chemotherapy is given depends on the type and stage of cancer being treated. Chemotherapy can be one or a combination of drugs.
- Targetted Therapy: have important role in advance/ metastatic disease. where medicine is given for specific receptors (targets) of cancer
- Immunotherapy: Acts with immune check points of cells and its role is emerging in colorectal cancer in specific patients.
Rehabilitation for Oral cancer Treatment
Rehabilitation may vary from person-to-person depending on the type of oral cancer treatment, and the location and extent of the cancer
Dietary counselling: many patients recovering from oral cancer surgery have difficulty eating, so it is often recommended that they eat small meals consisting of soft, moist foods.
Surgery: some patients may benefit from reconstructive or plastic surgery to restore the bones or tissues of the mouth, returning a more normal appearance.
Prosthesis: if reconstructive or plastic surgery is not an option, patients may benefit from dental or facial-part prosthesis to restore a more normal appearance. Special training may be needed to learn to use a prosthetic device.
Speech therapy: if a patient experiences difficulty in speaking following oral cancer treatment, speech therapy may help the patient relearn the process.
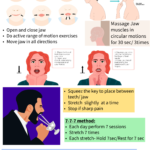
Jaw stretching exercises: Mouth Opening Exercises
Neck & Shoulder Range of motion exercises
Got some questions
- If all relavant examination and investigations has been done than plan of treatment is finalized with colon cancer surgeon
- After deciding surgical procedure cost estimate can be taken from billing department or hospital. Clinic or hospital department coordinator will assist in case any help required. +918750587489,
- you can visit nearby hospital for colonoscopy screening as advised in our screening section or you can read various society guidelines like American cancer society, USPTF.
- You can consult us through our online consultation link. https://api.whatsapp.com/send/?phone=918750587489&text=I+am+Looking+for+an+appointment+with+Dr.+Kaushal+Yadav.+Please+Help&type=phone_number&app_absent=0