Lung Cancer Prevent: Present Scenario
- Lung Cancer Prevent is most common cause of cancer related deaths, and it is the second most commonly diagnosed cancer worldwide with approximately 22 lakh new cases and 17.9 lakh deaths in 2020.
- Lung cancer is no 1 cause of cancer mortality, yet it is largely possible to prevent and eradicate lung cancer. Can We do That?
Contributing factors:
- Smoking is by far the leading cause of lung cancer, accounting for approximately 80% to 90% of cases. There is 20-fold increase in lung cancer risk in smokers compared to nonsmokers.
- Environmental tobacco smoke (ETS), also known as second-hand smoking: The risk for lung cancer is increased in nonsmokers who live with smokers, and it has been estimated that approximately 17% of lung cancers among never-smokers may be attributed to high levels of ETS during childhood and adolescence.
- Radon gas/ Indoor air pollution: Do you know that gas inside your home can be a risk factor for lung cancer development. Western data suggests Radon Gas as second leading cause of lung cancer. Radon is a gas formed from decaying of soil. It is present in buildings and is a contributor of indoor air pollution.
- Pollution: In India we don’t have data on radon indoor pollution, but we have an increasing and rising problem of Air Pollution. PM 2.5 is particulate matter in environmental air less than 2.5 micrometer. PM 2.5 excess can promote lung cancer. Sources includes construction sites, unpaved roads, fields fires, pollutants emitted from thermal power plants, industries and automobiles.
Pollution is contributor of 1 in 10 cases of lung cancer.
- air pollution includes combustion coal and wood for heating and cooking.
- Occupations with exposure to asbestos.
- Exposure to high doses of ionizing radiation.
Prevention: What can we do?
We have understood that most causes of lung cancer are related to the environment around us, so it is possible to decrease these causes and it requires effort at Individual, Society and National level.
- Avoid tobacco in any form, smoking/ chewing gutka/ hukka.
- Take every step to decrease air pollution. Increase green cover.
- Seal the cracks in building, open windows for cross ventilation, use indoor plants and air purifiers when required.
- Screening- Low Dose CT scan: Despite promising result and easy availability; acceptance for screening of lung cancer is very low around 2%. Early dtection is best cure and best prevention when it is in regard to cancer.
“Till we regularize policy for tobacco, till we regularize policies for construction and building, till we regularize policies for pollution, its not possible to eradicate lung cancer”
In short,
“ When a human first think that his action is not harming mother earth. When he thinks that his actions are not harming another human, only then it is possible to eliminate this fatal disease.”
Lung Cancer Prevention: Strategies to Reduce Risk
Lung cancer is one of the most common and deadly types of cancer worldwide. It occurs when abnormal cells in the lungs grow uncontrollably, forming tumors that can interfere with lung function and spread to other parts of the body. While anyone can develop lung cancer, certain factors significantly increase the risk. By understanding these risk factors and taking proactive steps, it is possible to prevent lung cancer and reduce its impact. This article explores various strategies to help prevent lung cancer and promote lung health.
Understanding Lung Cancer Risk Factors
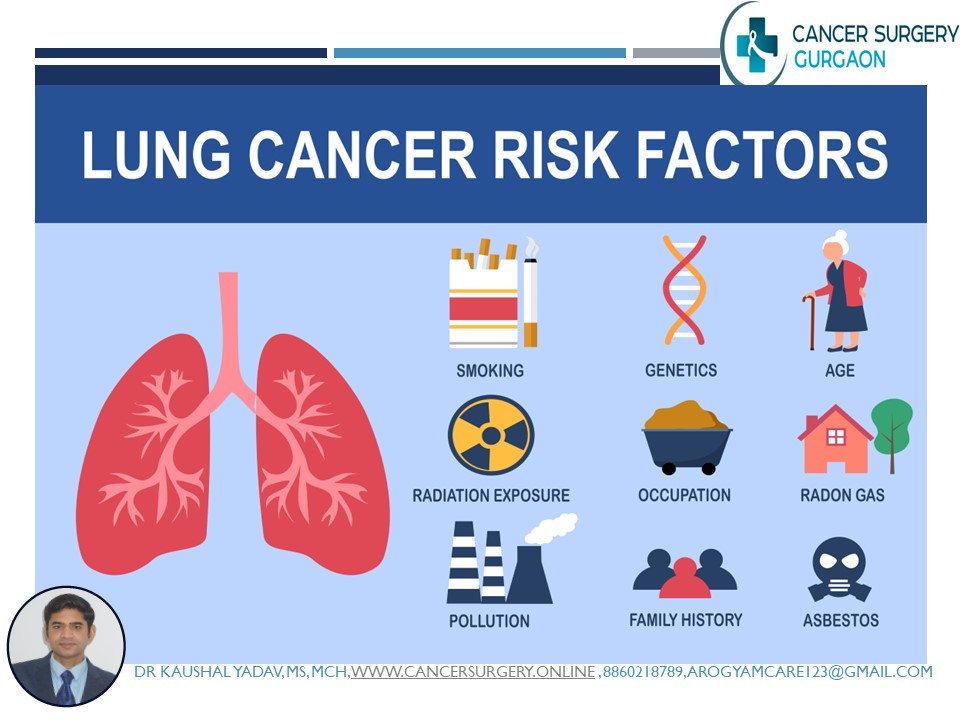
Lung cancer is primarily caused by exposure to harmful substances that damage the cells in the lungs. The most significant risk factors include:
Smoking: Cigarette smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer, responsible for approximately 85% of cases. The risk increases with the number of cigarettes smoked per day and the duration of smoking. Smokers are 15 to 30 times more likely to develop lung cancer than non-smokers.
Secondhand Smoke: Non-smokers exposed to secondhand smoke are at increased risk of lung cancer. Breathing in smoke from others’ cigarettes can still cause lung damage and cancer over time.
Radon Exposure: Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that can accumulate in homes, especially in basements and lower levels. Long-term exposure to high radon levels is the second leading cause of lung cancer.
Occupational Hazards: Exposure to certain chemicals and substances in the workplace, such as asbestos, arsenic, diesel exhaust, and certain industrial chemicals, can increase the risk of lung cancer.
Air Pollution: Long-term exposure to polluted air, especially in urban areas with high levels of smog, industrial emissions, and vehicle exhaust, is linked to an increased risk of lung cancer.
Family History: A family history of lung cancer may indicate a genetic predisposition to the disease, although lifestyle factors play a more significant role.
Personal Health History: Individuals with a history of lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or pulmonary fibrosis, have a higher risk of developing lung cancer.
Radiation Therapy: People who have undergone radiation therapy to the chest for other cancers may have an increased risk of lung cancer.
Strategies to Prevent Lung Cancer
Prevention is crucial in reducing the incidence of lung cancer and improving overall lung health. Here are some key strategies to help prevent lung cancer:
Avoid Smoking: The most effective way to prevent lung cancer is to never start smoking. For current smokers, quitting smoking is the single most important step to reduce the risk. Quitting smoking at any age can significantly lower the risk of lung cancer, improve lung function, and increase overall life expectancy. Various resources, such as nicotine replacement therapy, counseling, and support groups, can help individuals quit smoking.
Avoid Secondhand Smoke: Protect yourself and your loved ones from secondhand smoke by creating smoke-free environments at home, work, and public places. If you live with a smoker, encourage them to quit and ask them to smoke outside.
Test for Radon: Radon exposure is a preventable risk factor for lung cancer. Test your home for radon levels, especially if you live in an area known for high radon concentrations. Radon testing kits are available for purchase, and professional radon mitigation services can reduce radon levels if needed.
Protect Yourself at Work: If you work in an environment with potential exposure to harmful substances, follow safety guidelines and use protective equipment, such as masks and ventilation systems, to minimize exposure. Employers should provide proper training and safety measures to protect workers from hazardous materials.
Reduce Exposure to Air Pollution: Limit exposure to outdoor air pollution by staying indoors on days with high pollution levels. Use air purifiers at home to reduce indoor pollutants and avoid exercising outdoors in heavily polluted areas. Supporting clean energy initiatives and advocating for stricter air quality regulations can also help reduce overall air pollution.
Maintain a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce the risk of lung cancer. Antioxidants and nutrients in these foods help protect cells from damage and support overall health. Avoiding processed and red meats and limiting alcohol consumption can further reduce cancer risk.
Exercise Regularly: Physical activity promotes lung health and boosts the immune system, helping the body fight off infections and diseases. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week to maintain overall health and reduce cancer risk.
Get Regular Check-Ups: Regular medical check-ups can help detect early signs of lung problems and provide opportunities for discussing lung cancer risk factors with your healthcare provider. If you have a high risk of lung cancer, such as a history of heavy smoking, consider low-dose CT screening, which can detect lung cancer at earlier, more treatable stages.
Avoid Harmful Chemicals: Be cautious when using household chemicals, such as cleaning products and paints, which may contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can irritate the lungs. Use these products in well-ventilated areas and follow safety instructions.
Vaccinate Against Respiratory Infections: Chronic respiratory infections, such as pneumonia, can cause lung damage. Vaccination against flu and pneumonia, and practicing good hygiene, can help prevent respiratory infections and protect lung health.
The Role of Public Health Initiatives
Public health initiatives play a crucial role in lung cancer prevention by raising awareness, implementing policies, and providing resources to reduce risk factors. Some effective public health strategies include:
- Anti-Smoking Campaigns: Public education campaigns that highlight the dangers of smoking and provide support for quitting can help reduce smoking rates and prevent lung cancer.
- Smoke-Free Policies: Implementing and enforcing smoke-free laws in public places, workplaces, and multi-unit housing can reduce exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Radon Awareness and Testing Programs: Government initiatives that promote radon awareness and provide resources for testing and mitigation can help reduce radon-related lung cancer.
- Air Quality Regulations: Implementing and enforcing air quality standards can reduce pollution levels and protect public health.
- Workplace Safety Regulations: Establishing and enforcing safety regulations in industries with potential exposure to harmful substances can protect workers from lung cancer risk.
Conclusion
Preventing lung cancer is achievable through a combination of lifestyle changes, environmental awareness, and public health initiatives. By avoiding smoking, protecting against secondhand smoke, reducing exposure to radon and air pollution, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can significantly lower their risk of developing lung cancer. Public health efforts to promote education, enforce regulations, and provide resources are essential to reducing lung cancer incidence and saving lives. Together, we can work towards a future where lung cancer is less common and more preventable.
To Know more about Lung Cancer:
Discover more from CancerSurgery
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.




