Uterus (Endometrium) Cancer
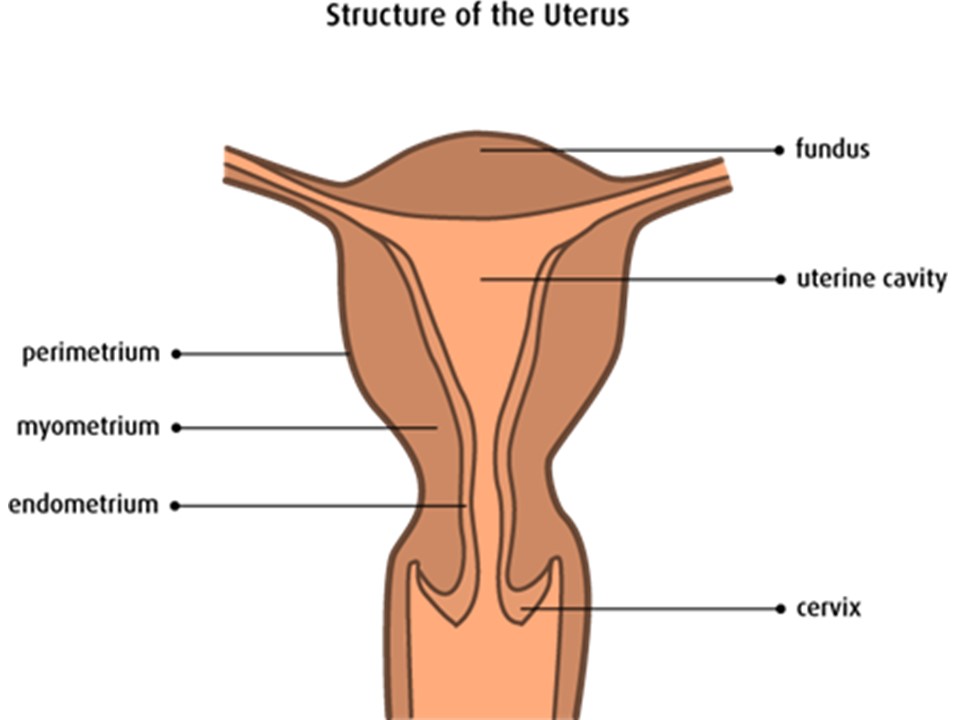
Uterus is an inverted pear-shaped muscular organ of the female reproductive system, located between the bladder and the rectum. Its function is to implant and nourish the fertilized egg until the fetus, or offspring, is ready to be delivered. Its parts include fundus, body, isthmus & cervix. Uterine cavity along with vagina forms the birth canal. Inner most layer of uterus is endometrium, where most of cancers arise. Middle layer is muscle layer; myometrium and outermost layer is perimetrium, serosa.
- Uterus cancer is most common gynecological cancer globally. In India uterus 4th most common cancer of females.
- Uterine cervix is lowermost part of uterus. Carcinoma of uterine cervix is second most common cancer in Indian females after breast cancer and it is most common female cancer in rural parts of India.
- Incidence of endometrium cancer is in rising trend.
Types
- Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma: most common type, 80-90%. It originates in the cells of inner lining of uterus; the endometrium.
- Sarcoma: rare form that develop from muscle or connective tissue of the uterus.
- leiomyosarcoma – arising from smooth muscle cells.
- endometrial stromal sarcoma – developing from the connective tissue of the endometrium.
- Carcinosarcoma (also known as Malignant Mixed Mullerian Tumor or MMMT): less common and more aggressive form.
- Clear Cell Carcinoma: rare
- Serous Carcinoma: less common and more aggressive type.
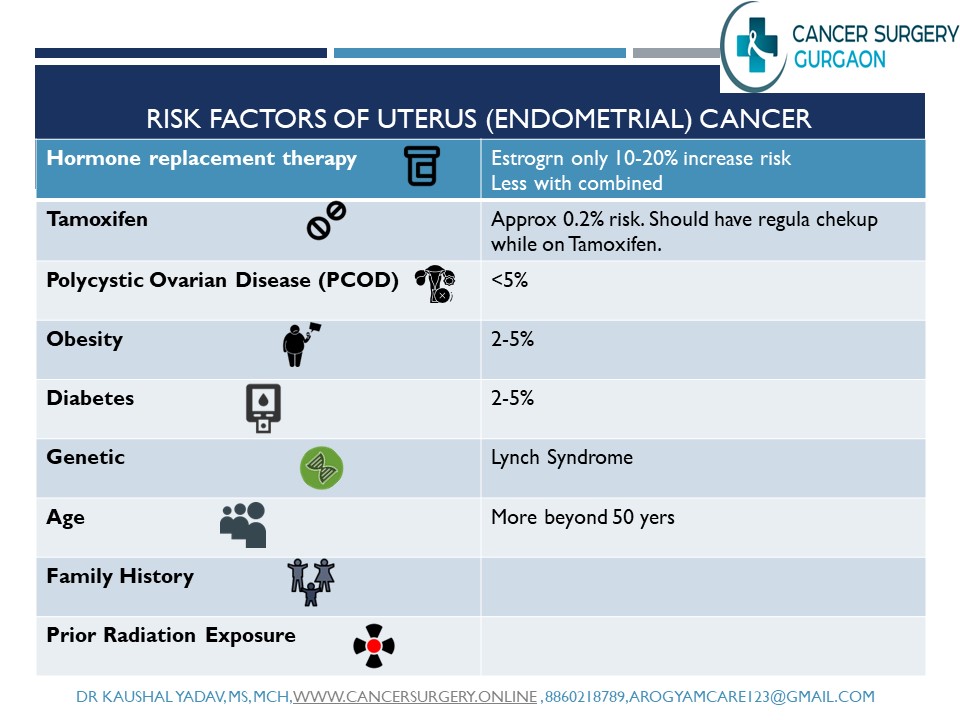
Risk Factors
- Age: Uterine cancer is more common in women over 50, especially after menopause.
- Obesity: Excess body fat can increase estrogen levels, which can stimulate the growth of abnormal cells in the endometrium.
- Hormone therapy: Taking estrogen alone or with progestin for menopausal symptoms can increase the risk of endometrial cancer, especially if taken for a long time (beyond 5 years) or at high doses.
- Tamoxifen: This drug is used to treat breast cancer, but it can also act like estrogen on the endometrium and increase the risk of endometrial cancer.
- Family history: Having a close relative with uterine cancer or a hereditary syndrome such as Lynch syndrome or Cowden syndrome can increase the risk of uterine cancer.
- Other medical conditions: Having diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometrial hyperplasia (thickening of the endometrium), or a history of ovarian or breast cancer can increase the risk of uterine cancer.
Screening for Uterus Cancer:
There is no standard screening test for uterine cancer. Annual gynecological examination is recommended for females.
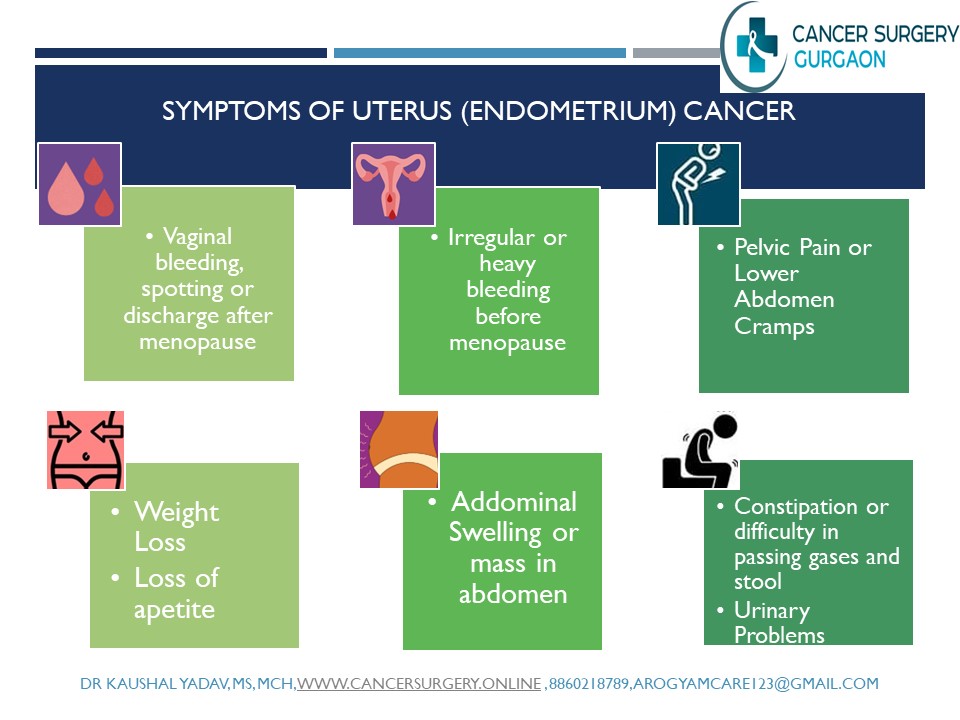
Alarmimg Signs and Symptoms of Uterine Cancer
Investigations
Endometrial biopsy: A small piece of tissue is removed from the endometrium and examined under a microscope for signs of cancer.
ultrasound
Hysteroscopy: A thin tube with a light and a camera is inserted through the cervix and into the uterus to look for any abnormal areas and biopsy is taken.
Dilation and curettage (D&C)
Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, or PET scans to see if the cancer spread.
Treatment
Surgery: Surgery is mainstay of treatment. total hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, with or without lymph node dissection
- Surgical staging with Hysterectomy with bilateral Salphingo-oophrectomy: removes uterus and bilateral tubes and ovaries.
- Pelvic and/ or Paraaotic Lymph Node Dissection: may be avoided in very early stage, but in advance disease or lymph node positive disease always done.
- Omentum removal (omentectomy): in high grade tumors
- Open Approach
- Laparoscopic Approach
- Robotic approach
First goal of surgery is complete removal of disease with lymph nodes and areas of spread. In advance case if it is found that laparoscopic or robotic approach has difficulties in removing complete disease it always better and recommended to utilize open approach.
Some of the benefits of minimally invasive surgery (MIS) compared to open surgery are reduced blood loss, shorter hospital stay, lower postoperative morbidity, and faster recovery. However, MIS may also have some limitations, such as longer operative time, higher cost, and potential technical difficulties. Therefore, it is important to individualize the surgical approach for each patient with carcinoma endometrium, taking into account the evidence-based guidelines and the patient’s preferences.
To Book Appointment for Cancer Surgery :
Integration of Multimodality Treatment
Radiation therapy: High-energy rays or particles are used to kill or shrink cancer cells. Radiation therapy can be given externally (from a machine outside the body) or internally (by placing radioactive sources inside or near the tumor). Radiation therapy is usually given after surgery in high-risk cancer.
Chemotherapy: Drugs are used to kill or stop the growth of cancer cells. Chemotherapy may be used after surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence, or for advanced or recurrent uterine cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
Hormone therapy: Drugs are used to block or lower the amount of estrogen or progesterone in the body, which can slow down or stop the growth of some types of uterine cancer. Hormone therapy may be used for advanced or recurrent uterine cancer that is hormone receptor positive, or to relieve symptoms such as bleeding or pain.
Targeted therapy: Drugs are used to target specific molecules or pathways that are involved in the growth and survival of cancer cells. Targeted therapy may be used for advanced or recurrent uterine cancer that has certain genetic mutations or markers.
Got some questions
- If all relavant examination and investigations has been done than plan of treatment is finalized with colon cancer surgeon
- After deciding surgical procedure cost estimate can be taken from billing department or hospital. Clinic or hospital department coordinator will assist in case any help required. +918750587489,
- you can visit nearby hospital for colonoscopy screening as advised in our screening section or you can read various society guidelines like American cancer society, USPTF.
- You can consult us through our online consultation link. https://api.whatsapp.com/send/?phone=918750587489&text=I+am+Looking+for+an+appointment+with+Dr.+Kaushal+Yadav.+Please+Help&type=phone_number&app_absent=0