Colon Cancer
What is colon cancer?
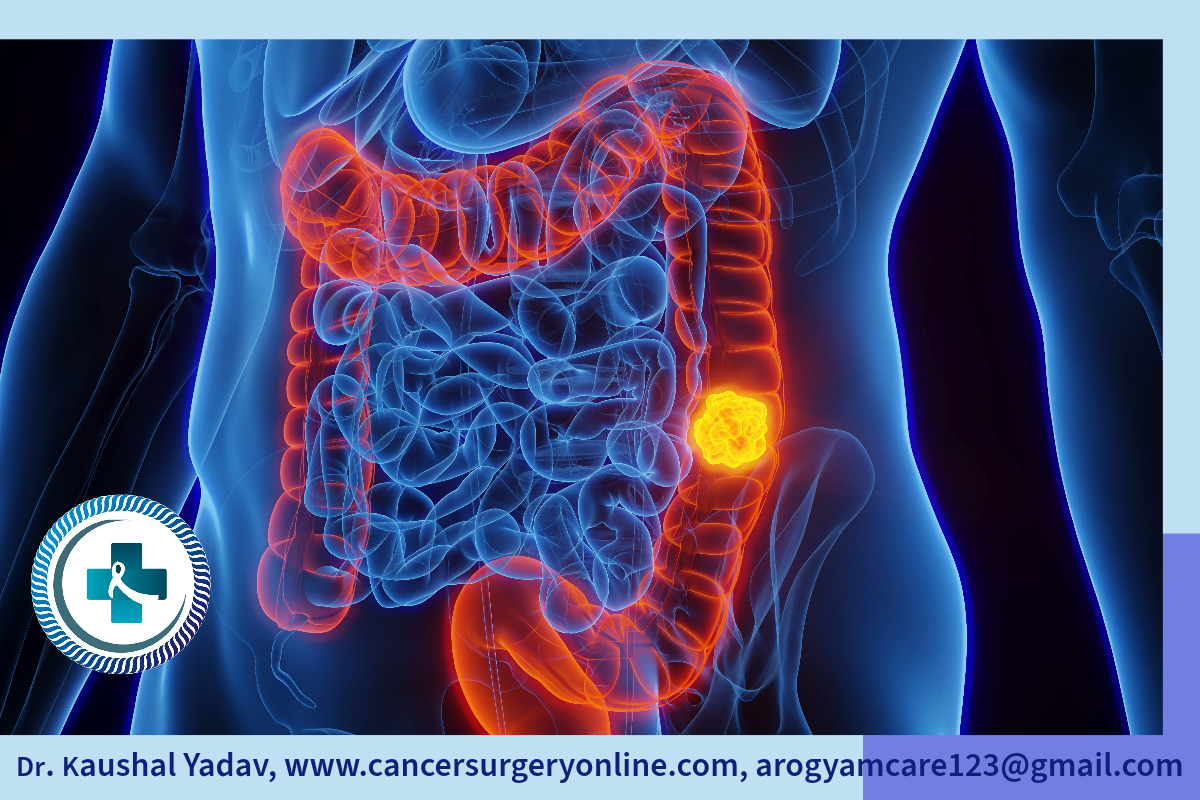
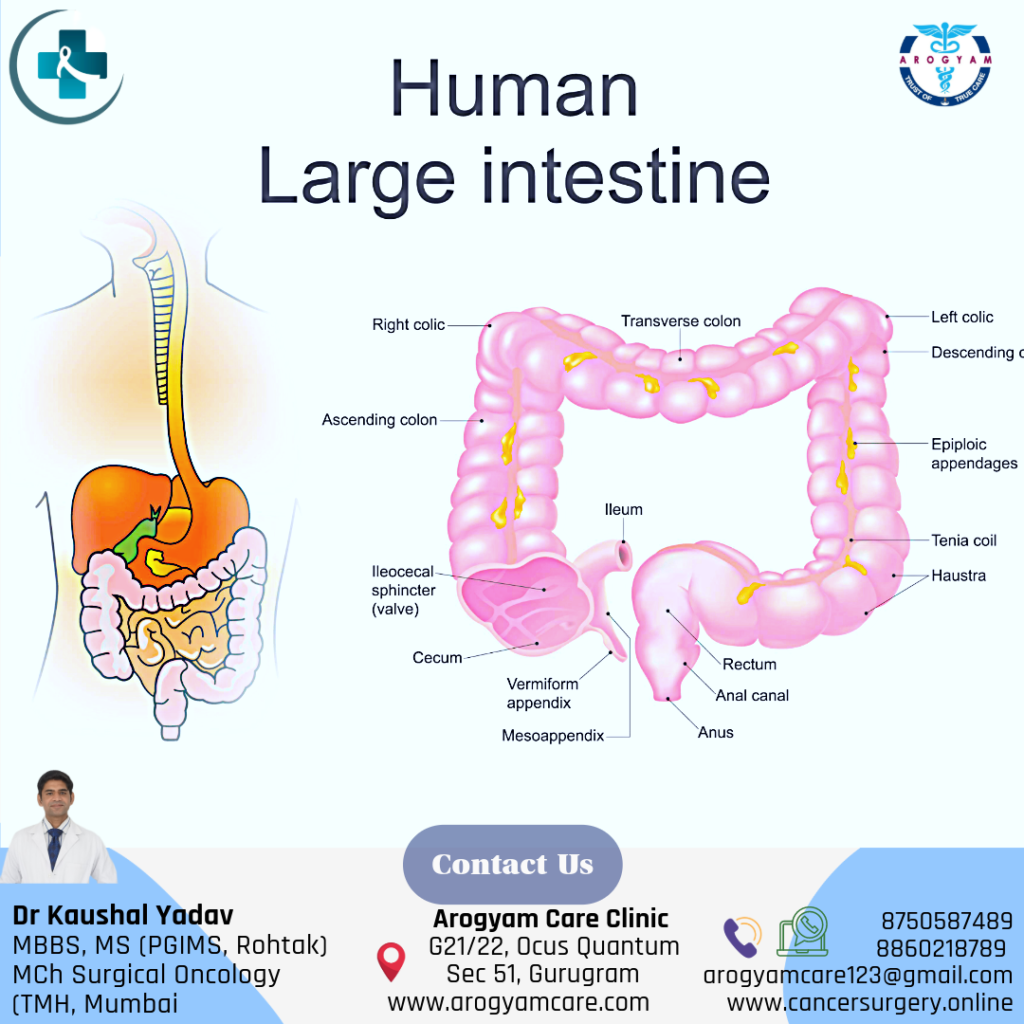
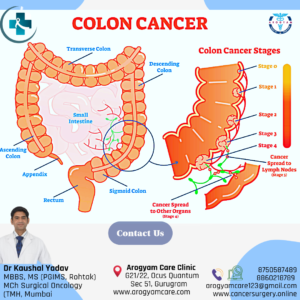
Large intestine is approx. 1.5 meter long and most of part is colon. 1st part is ascending colon, small intestine continues in Caecum which is initial part of ascending colon. 2nd part is transverse colon, 3rd part is descending colon because it continues downward in 4th part called sigmoid colon. Sigmoid colon continues in last part of large intestine called rectum, most of which is deep in pelvis. Food nutrients get absorbed in small intestine and residue reaches in colon where water is absorbed. The stool formed is hold in rectum until passed out through anus. Understanding of anal sphincter is very important in management of rectum cancer.
Colorectal cancers together are the 3rd most common cancer and 2nd most common cause of cancer related mortality globally. In India it is 6th most common cancer group and 7th most common cause of cancer related mortality.
Types of colon cancer
- Adenocarcinoma: The vast majority of colon cancers are adenocarcinomas. This type of cancer develops from cells that line the inside of the colon and rectum.
- Other types: these includes neuroendocrine tumors, which develop from hormone-producing cells, and gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), which develop from connective tissue cells in the GI tract.
Risk Factors or causes of colon cancer, large intestine cancer
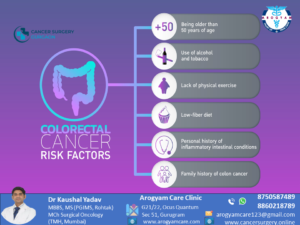
Age: Colon cancer risk increase beyond 50 years of age. In recent era colon cancer risk is also increasing in 30-40- and 40-50-years age group. With each new generation this age group for risk of cancer is decreasing. Colon cancer is increasing in younger people age group because of exposure to risk factors happening early in life.
- Diet and colon cancer: Processed food/ low fiber diet and junk foods are important cause of rising cases of colon cancer.
- Obesity/ overweight
- Red meat: Eating every 100g of red meat increases the risk of colon cancer up to 17%.
- Processed meat consumption. Every 50g consumption of processed meat increase the risk of colorectal cancer by 20%.
- Tobacco
- Alcohol: No amount of alcohol intake is safe. Even small amount of alcohol increases the risk of colorectal cancer by 1.5 times and this risk increase with amount of alcohol intake.
- Inflammatory bowel disease- anyone with inflammatory bowel disease need to start getting screened for colorectal cancer at early age and more often because inflammatory bowel disease is a risk factor for colon cancer.
- Family history of colorectal cancer or polyp.
- Personal history of colorectal cancer or Polyp
- Genetic Cancer Syndromes: Lynch syndrome (hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer, or HNPCC) and familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
*Diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, fibers and that limits or avoids red and processed meats and sugary drinks probably lowers risk the risk colorectal cancer.
Screening/ health ckeckup to detect colon cancer early:
The American Cancer Society recommends that colon cancer screening for people with average risk should start regular screening at age 45. This can be done either with a stool-based test to detect blood or by colonoscopy. People in good health should continue regular colorectal cancer screening up to 75 years. Between 76 – 85 years screening should be based on person’s preferences, overall health, and prior screening history. Beyond 85 years colorectal cancer screening usually not recommended.
Usually recommended tests are:
- Stool Tests: Fecal Immunohistochemical Test (FIT) & Fecal Occult Blood test (FOBT) – Stool based test once a year can decrease colorectal cancer morality by 30%.
- Colonoscopy: Colonoscopy is an endoscopic examination to check inside of large intestine. Colonoscopy once in every 10 years decrease colorectal cancer related mortality by 50%.
- CT colonography (virtual colonoscopy) every 5 years in patients not opting colonoscopy as alternative method.
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy every 5 years.
For persons with high risk or family history of colon cancer screening and cancer checkup tests are recommended to start early and more frequently with advice from treating oncologist for colon cancer.
Alarmimg Signs of Colon Cancer/ Symptoms of colon cancer
Warning signs and symptoms of colon cancer as suggested by senior oncologist in Delhi NCR includes. Symptoms of colon cancer in women and men are same.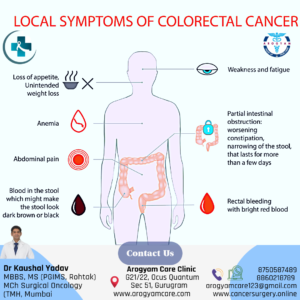
- Changes in bowel habits i.e. constipation or diarrhea that lasts longer than usual or not getting relieved should be checked properly.
- Changes in stool color
- Changes in stool shape, such as narrowed stool
- Blood in the stool
- Bleeding from the rectum
- Excessive gas
- Abdominal cramps
- Unexplained weight loss, fatigue, loss of appetite
- Difficulty in passing stool and gases. May cause intestinal obstruction if bulky growth.
- Anemia or low hemoglobin leading to fatigue or low energy.
Colon cancer incidence is also rising in younger adults. Symptoms of colon cancer in young adults are same as described so if these symptoms are not not getting corrected proper investigations should be done.
Investigations for diagnosis of colon cancer
- Colonoscopy and Biopsy
- CT scan for disease extent evaluation
- PET- CECT (PET Scan) is done to check spread of disease in colon and nearby organs and disease spread in other organs.
- Tumor markers: most commonly done blood tumor marker test for colon cancer is CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen). It also helps in followup checkup after treatment of colon cancer.
- Genetic testing may be advised in younger patients less than 50 years and patients with family history of colon cancer or colon polyps.
Treatment of colon cancer
Surgery: surgery is the mainstay of treatment among colon cancer treatment options. Colectomy is advised by oncologist for treatment of colon cancer.
- Radical Hemicolectomy with Intestinal anastomosis: is most commonly performed surgery which removes that segment of affected colon along with all lymph nodes and vascular supply and rejoin proximal and distal ends of intestine
- Right Hemicolectomy/ Extended Right Hemicolectomy with Ileocolic (Small Bowel with large bowel) Anastomosis: is the surgery for cancer located in initial part of large intestine (Caecum & Ascending colon).
- Transverse Colectomy: for cancer located in mid-part of large intestine.
- Left Hemicolectomy/ Extended left Hemicolectomy: is the surgery for colon cancer located in left side of colon. Initial and lower part of colon are joined.
- Sigmoid Colectomy: for cancer located in last part (sigmoid colon) of large intestine. Colon is anastomosed with upper rectum.
- Anterior Resection: cancer located in lower part of colon or at junction of colon and rectum also involved removal of initial part of rectum along with sigmoid colon. Colon is joined with lower rectum.
Open, laparoscopic surgery for colon cancer and robotic surgery for colon cancer are done by Surgical Oncologist.
Short-term temporary stoma (ileostomy) may be made in case of frail patients or difficult anastomosis. – end of the intestine is brought out through a hole in the skin of the abdomen. This gives time to intestine for healing before stool moves through it. Mostly stoma is reversed (the intestines reconnected) after adequate healing.
- Total coloectomy/ proctocolectomy: If there are multiple sites of cancer in colon or associated multiple polyps in colon. In case of genetic risk factor like Hereditary predisposing conditions like HNPCC (Lynch syndrome), APC colorectal cancer mutation complete colon and rectum are removed. Small intestined is joined with anal canal.
- Metastatectomy: if colon or rectal cancer has spread to limited organ like Liver or lung and complete excision of metastasis is possible.
- Cytoreductive surgery + Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal chemotherapy (CRS+HIPEC): when there is peritoneal (inner covering of abdomen) only metastasis extensive surgery is done to completely remove the disease followed by intraperitoneal instillation of heated chemotherapy during surgery.
Right hemicolectomy for Ascending Colon Cancer
Left hemicolectomy for Ascending Colon Cancer
Transverse Colectomy for mid transverse Colon Cancer
Sigmoid Colectomy for sigmoid Colon Cancer
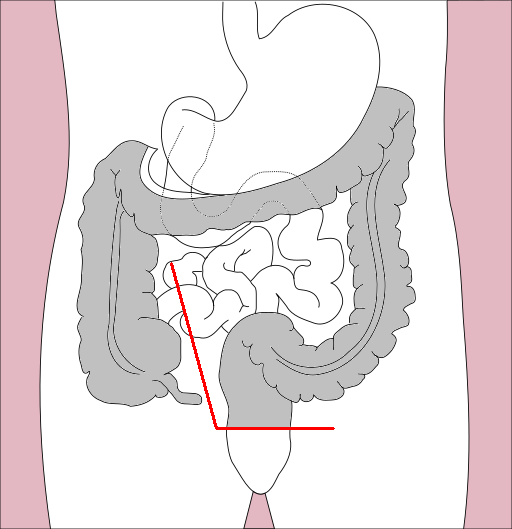
Total Colectomy multiple Colon Cancer or colorectal polyp
by Cancer Research UK is licensed under <a href=”https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0″ target=”_blank” rel=”noopener noreferrer”>CC BY-SA 4.0</a>
“noopener noreferrer”>EvanWorse</a> is licensed under <a href=”https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/” target=”_blank” rel=”noopener noreferrer”>CC BY-SA 4.0</a>
To Book Appointment for Cancer Surgery :
Integration of Multimodality Treatment, Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy for Colon cancer
- Chemotherapy:
Usually given after surgery in advance colon cancer or cancer with high risk features for better long term control.
Sometimes chemotherapy also given before surgery in borderline curable case to decrease size of disease.
In metastatic stage IV disease chemotherapy is primary disease
- Targetted Therapy: have important role in advance/ metastatic disease. where medicine is given for specific receptors (targets) of cancer
- Immunotherapy: Acts with immune check points of cells and its role is emerging in colorectal cancer in specific patients.
- Radiation Therapy: Raditaion therapy is helpful when there is residual microscopic disease after surgery.
Request an appointment with expert cancer surgeon in laparoscopic or robotic colon cancer surgery
You can make an appointment with Dr Kaushal Yadav by:
● Scheduling an Online Consultation.
● Requesting an online second opinion from our specialists by sharing reports
● Writing on email id: arogyamcare123@gmail.com or whatsapp on +918750587489
To speak to someone directly, please call on +91 87505 87489 If you have symptoms of an urgent nature, please go to the emergency room immediately.
Got some questions
- If all relavant examination and investigations has been done than plan of treatment is finalized with colon cancer surgeon
- After deciding surgical procedure cost estimate can be taken from billing department or hospital. Clinic or hospital department coordinator will assist in case any help required. +918750587489,
- you can visit nearby hospital for colonoscopy screening as advised in our screening section or you can read various society guidelines like American cancer society, USPTF.
- You can consult us through our online consultation link. https://api.whatsapp.com/send/?phone=918750587489&text=I+am+Looking+for+an+appointment+with+Dr.+Kaushal+Yadav.+Please+Help&type=phone_number&app_absent=0
Best Doctor for colon cancer treatment in Gurgaon says for colon cancer, the overall 5-year survival rate for people is 67%. If the cancer is diagnosed locally, the survival rate is 89%. If the cancer has spread to surrounding tissues or organs and / or regional lymph nodes, the 5-year survival rate is 72%
Red meat refers to meat from muscle of mammals like beef, veal, pork, lamb, mutton, horse, and goat.
Submit Your Query Here & We'll Get Back
To Book Appointment for Cancer Surgery :
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.