Pancreas Cancer
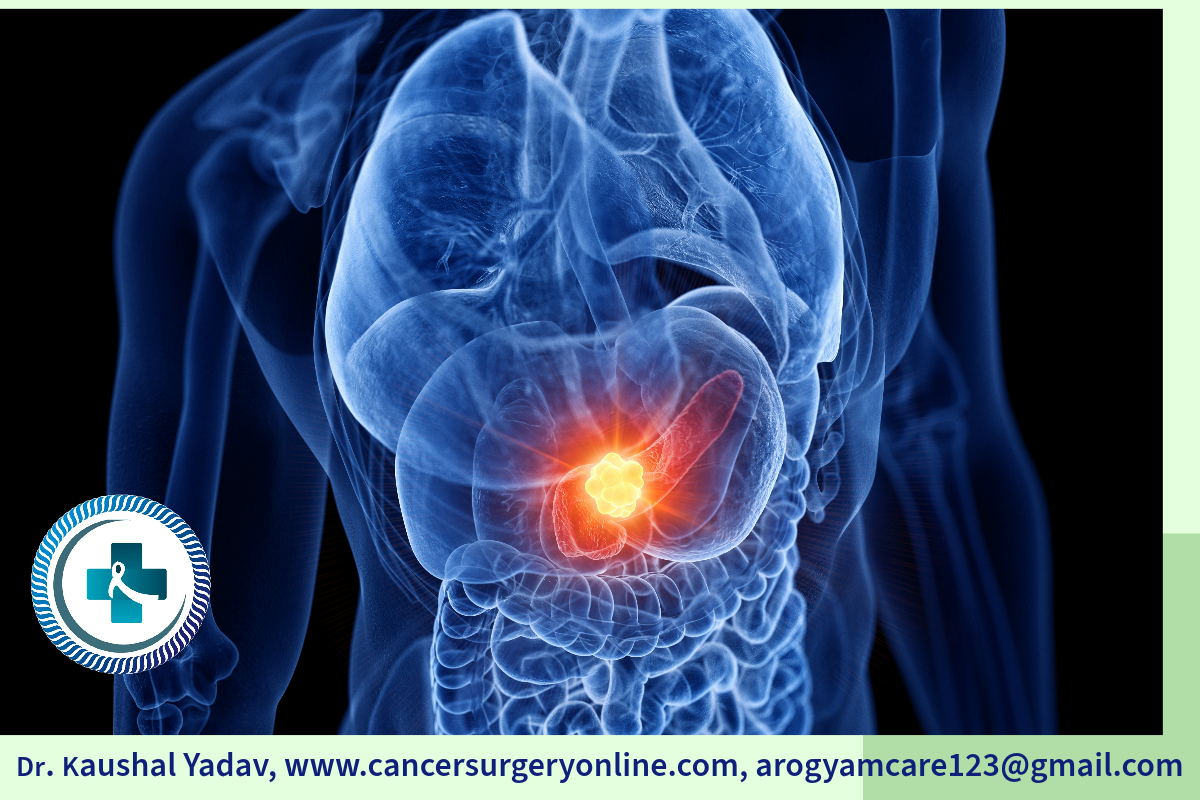
The pancreas is a gland that is shaped like a thin pear lying on its side. The wider end of the pancreas is called the head, the middle section is called the body, and the narrow end is called the tail. The pancreas lies with C loop of first part of small intestine called duodenum and situated between the stomach and the spine. Enzymes are released in pancreatic secretions which helps in digestion of food. It produces hormones which control blood sugar i.e., insulin and glucagon. Pancreatic cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the pancreas.
Types
- Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma – most common type. Arise from cells within pancreatic duct- Pancreatic Duct Adenocarcinoma.
- Periampullary carcinoma
- Adeosquamous/ Undifferentiated carcinoma
- Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Carcinoma/ Tumors
- Cystic Neoplasm of pancreas.
Risk Factors
● Old Age
● Tobacco
● Heavy alcohol use
● Overweight/ Obesity
● Diabetes
● Chronic Pancreatitis
● Family History
● Red and processed meats (such as sausage and bacon), saturated fats, Sugary drinks may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer.
Genetic conditions:
● Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) syndrome.
● Hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC; Lynch syndrome).
● Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome.
● Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
● Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome.
● Familial atypical multiple mole melanoma (FAMMM) syndrome.
● Ataxia-telangiectasia
Alarmimg Symptoms of Pancreas/ Pancreatic Cancer
Initial symptoms of pancreatic cancer are usually not present. In 80% of cases disease has already present in advance stages. Because of late presentation and highly aggressive nature, pancreatic cancer has high mortality rate.
● Abdomen/ back pain
● Yellowish discoloration of body and secretions called jaundice. It is present in around 70% of cases.
● low appetite and weight loss
● pale gray or fatty stool/ Dark colored urine
● nausea and vomiting
● Unexplained weight loss/ Loss of appetite/ fatigue
● diarrhea or constipation
● Indigestion
● Rarely a new onset diabetes
● Itching due to jaundice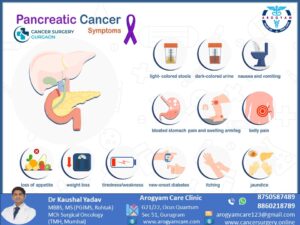
Investigations
- CECT/ MRI/ PET CECT scan: to get a complete and detailed extent of disease within and outside pancreas
- Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)/ Upper GI Endoscopy: get images of pancreas and biopsy can be done. When jaundice is very high or patient not suitable for Surgery ERCP+ stenting is done,.
- Tumor marker: CA 19-9
Treatment
Surgery: When cancer is localized in pancreas, it is possible to eliminate the cancer cells by removing all or part of the pancreas. Surgery is the only curative option available for pancreatic cancer.
The three main surgical procedures for pancreatic cancer are:
● Whipple procedure/ Pancreaticoduodenectomy: Portion of disease bearing pancreatic head, along with a portion of the stomach, duodenum, bile duct and lymph nodes are excised with anastomosis to restore normal passage.
● Distal pancreatectomy: Disease bearing last part of the pancreas and usually spleen are removed.
● Total pancreatectomy: rarely done surgery, entire pancreas and spleen are removed. Post pancreatectomy diabetes may develop.
Palliative surgery: Palliative surgery can help relieve symptoms such as obstructions in the bile duct or duodenum. Bypass so that bile can continue to flow from the liver- Hepaticojejunostomy. Another option is to insert a small stent in the bile duct to keep it open. This is a less invasive procedure using an endoscope. Palliative Gastrojejunostomy to relieve stomach obstruction is also required in some cases.
To Book Appointment for Cancer Surgery :
Integration of Multimodality Treatment
- Chemotherapy: Given as adjuvant treatement after aurgery in advance cases, sometimes as Neoadjuvant treatment. In advance metastatic cases palliative chemotherapy is given.
- Targeted therapy: There are different types of targeted therapy, such as:
● EGFR inhibitors, which block the EGFR protein
● PARP inhibitors, which block PARP enzymes
● NTRK inhibitors
These drugs hit specific targets, so side effects are less.
Immunotherapy: It helps the body’s immune system to recognize and kill cancer cells. PD-1/ PDL 1 inhibitors are type of immunotherapy against pancreatic cancer.
Radiation therapy: High energy rays are given on the cancer cells. May given before surgery in borderline operable cases or after surgery in advance cases. May be an option in localized disease when patient is not fit enough to undergo surgery.
Related Video
Got some questions
Pancreas is situated deep inside body behind abdominal organs. So it doesn’t produce any specific symptom initially. Also there are no approved screening tests for pancreas cancer. When it grows it produce symptoms; but by then it is late in most of cases. More than 80% cases present in last stage
Don’t ignore even the mild initial symptoms, do take self medicines, visit your doctor, discuss with them and if required do appropriate investigations. At present there is no recommended screening methos and no chekup advised for sake of pancreas cancer. But if doubt by doctor as per history and complaint of patient than CT scan can be advised especially in high risk group.
Unless and until detected in early stage when surgery is possible; pancreas cancer cannot be cured. So, every attempt should be made to not miss the early window of care and appropriate treatment should be followed earliest possible.
Survival rate of pancreas cancer is very poor with average of 12% at 5 years. For localized disease 5 year survival is 44% and for metastatic disease survival rate is <3%
No cancer is good. There are certain body cancers which give less opportunity of care and most of time undetectable initially. These include Pancreas cancer, gall Bladder cancer, Cholangicarcioma. .Contact Dr Kaushal Yadav for Cancer Surgery & treatment in Gurgaon, Delhi-NCR, India

